The Challenges and Triumphs of Deploying Artificial Satellites
Our forefathers would look at the moon and star with curiosity as they tried to unravel what was out in space. Today, we have created more ‘moons’ in the form of artificial satellites in the cosmic void. These engineering wonders float around our planet, unnoticed but constantly influencing the world we live in today. Whenever the first artificial satellite known as Sputnik made its way into the cosmos in the year 1957, the world opened up what would come to be referred to as the Satellite Era.
Artificial satellites enable us to get connected, be informed, and provide an understanding of our planet and space beyond our Earth like never before. On matters ranging from communication and navigation to meteorology and scientific research, artificial satellites have become important in many facets of contemporary existence.
Definition
An artificial satellite can be described as an object/spacecraft that is placed in space to revolve around the earth with a specific mission to accomplish. It is like a human-made moon, a sophisticated machine designed to serve a specific purpose. Think of it as a sophisticated robot sent into space, carrying instruments and systems to do things like relay communications, monitor weather, or explore the cosmos.
Types of Artificial Satellites
Artificial satellites have a diverse range of types, each with unique capabilities and functions:
- Communication Satellites: These satellites provide the physical infrastructure for Global communication system. They transmit television signals, provide internet connection and allow for telephone conversation across the country or even the world, which in essence brings the world closer by providing instant communication.
- Navigation Satellites: The best example of navigation satellites at work would be GPS. These satellites offer accurate positioning or timing services for car, boat, aircraft and for persons with handy gadgets.
- Earth Observation Satellites: Such satellites are constantly observing our planet and they are helpful in meteorological forecasts, research of the environment, and struggle with catastrophes. These provide information on factors such as; weather, temperature, rainfall, rate of deforestation and the likes.

- Scientific Satellites: Exploring the mysteries of space to learning about the climate of our own planet, scientific satellites are valuable in their role of instruments for scientific studies. An example is Hubble Space Telescope used for deep space observation and for weather prediction.
- Military Satellites: Used in spying, reconnaissance, and as communicational aids, military satellites serve as essential tools in defense mechanisms of various countries. The exact abilities may be explained and concealed, however their role in international relations cannot be overestimated.

Launching Satellites into Space
Launching and maintaining a satellite in orbit requires a complex interplay of engineering and physics:
- Orbital Mechanics and Types of Orbits: Depending on the function the satellites perform they are located at specific orbits. Some of the well-known orbits include Low Earth Orbit frequently abbreviated as LEO, Medium Earth Orbit abbreviated as MEO, and Geostationary Orbit commonly known as GEO. Each orbit has his pro and cons concerning the scope, delay, and the need for mid-course corrections.
- Satellite Launch and Deployment: This is because merely getting the satellite to the outer space means that one has to overcome the force of gravity of the earth and this requires powerful rockets. Satellites are then carefully ‘released’ from their ‘rockets’ and carefully moved to and placed in specific orbits.
- Satellite Components: Dependent on the design, a typical satellite comprises the power system (frequently solar panels), the communication system (antennas and transponders), the attitude control system for orientation and the payload or the useful load which is comprised mostly of scientific instruments, cameras, and other devices.
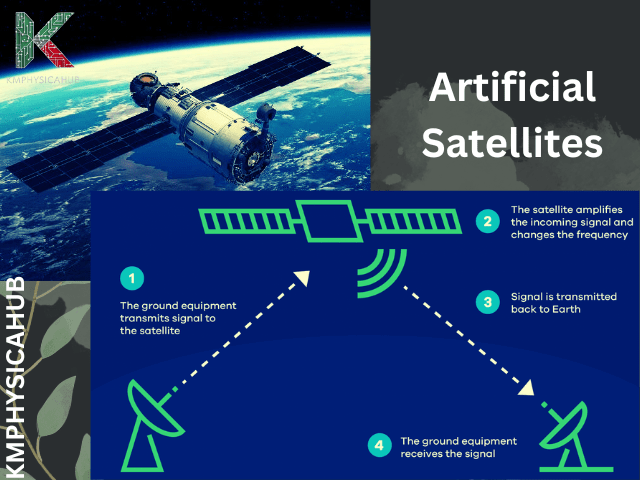
- Data Transmission and Ground Stations: Using radio waves, satellites record data and then send the data back to earth. This data is received, processed, and disseminated by ground stations situated worldwide to the intended consumers.
Applications and Benefits of Artificial Satellites
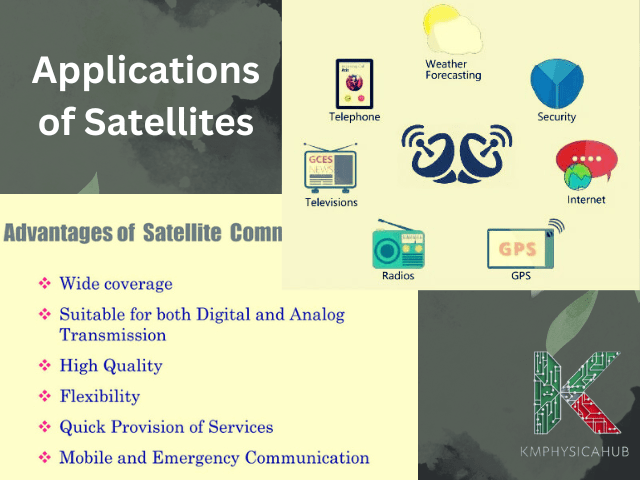
Communication & Globalization: They enable easier ways of transmitting information to the far ends of the earth making the world seem to have come closer. These are very important for telephone communications, information on the Internet, Television broadcasting and even in the most remote areas of the world. This has created globalization, as people and cultures have formed an association, never seen before.
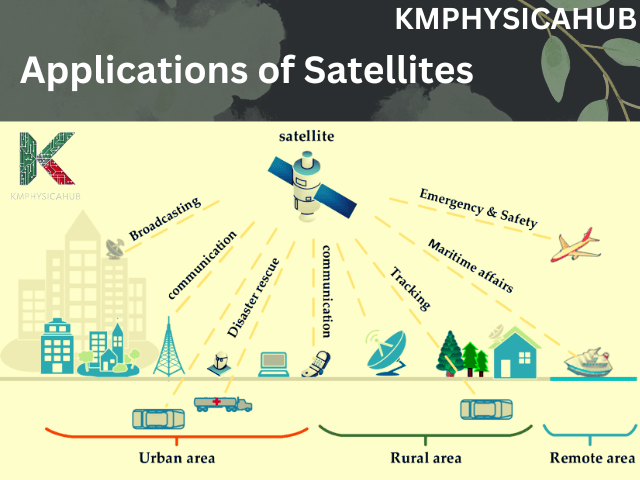
Navigation & Precision Technologies: Current uses of GPS and other satellite navigation systems are uncountable, and they range from simple car navigation to high-tech applications such as precision agriculture and emergency response services. It plays a crucial role in delivery services, transportation, geographical representation and analyzing the environment.
Earth Observation & Environmental Awareness: They watch over our world and the climate changes, deforestation, pollution and many others. It is needed for predicting the weather, disaster management, environmental conservation, and carrying out extensive studies in numerous disciplines.
Scientific Discovery & Exploration: From Hubble Space Telescope exploring the far-reaching ends of infinity to investigating the moons of Mars and numerous other missions, satellites have transformed the fields of astronomy, astrophysics and the notions about the universe. They also serve as crucial metadata for climate and earth science applications.
National Security & Geopolitics: Even they are operated secretly, military satellites play a critical role in global affairs. It offers information gathering, observation and safe means of communication to defense forces across the globe, thus determining military tactics and policies, and also the international politics.
Economic Growth & Innovation: The satellite industry is also a facilitator for growth because it promotes development in aerospace engineering, telecommunications, data science, and other fields. It is also important to note that satellite information and service benefits many sectors such as agriculture, transport, banking and entertainment among others.
Challenges Faced due to Artificial Satellites
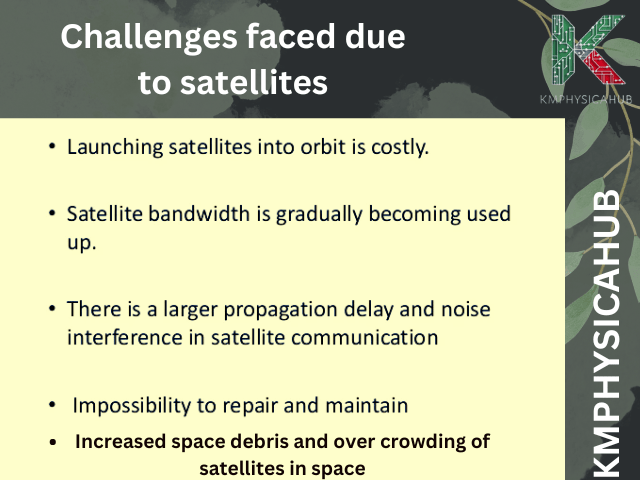
- Space Debris; A Cosmic Junkyard: Each launch contributes to the space debris population, which comprises failed satellites, discarded rocket boosters, and even shards from impact. This space debris presents a substantial threat to working satellites, and can even cause chain reactions of satellite collisions known as Kessler Syndrome, which threatens the functionality of our space equipment. It is necessary to underline the significance of the international cooperation and search for new approaches to enhance debris removal.
- Orbital Crowding and Spectrum Management: Having thousands of satellites in orbit and intending to send thousands more, the task of coordinating this chaos in space is critically important. The most crucial operational requirement includes the appropriate distribution of orbit locations and the assignment of radio-frequency bands that are used for broadcasting in order to avoid interference and the probable degradation of the operational functionality of satellites.
- Cost of Satellite Development and Launch: Orbital space is not readily accessible to everyone, because the creation of satellites and their launch requires lots of money and technical know-how. But such factors as the miniaturization of satellites and reusable launch vehicles which are now in development, point to the fact that the barriers to affordability are likely to come down in the future.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Satellite Era
Artificial satellites today have become essential to the functioning of the contemporary world, as they allow people to communicate across continents, study the Earth’s state, and explore the universe. They affect communication, navigation, Earth observation, scientific discovery, and national security at large in immense ways. With the advancement of the world into the further part of the 21st century, the Satellite Era will indeed play significant roles in molding the future. The problems are out there, but so are the opportunities for creativity and cooperation that will ultimately drive global progress. It means that the further development of space exploration, and moreover the further evolution of mankind, depends on these ‘spaceships’ that we have put into the space.
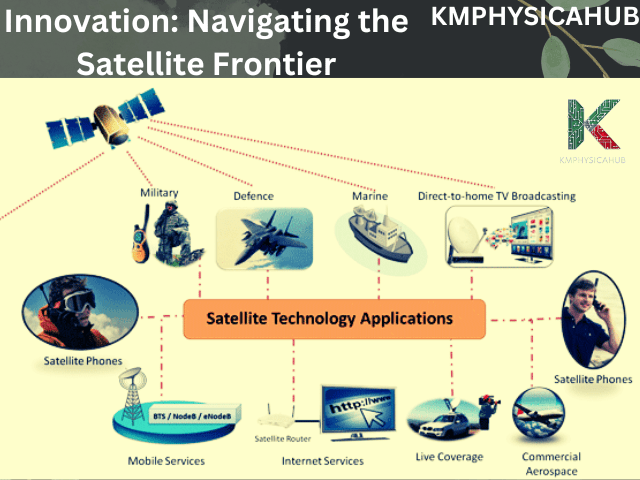
Future Trends: Navigating the Artificial Satellite Frontier
Advancements in Satellite Technology: Satellites’ future appears to be filled with great promises. Advancements have resulted to smaller satellites that are more capable. Machine learning is improving data analysis and automation. There are new materials in development as well as new types of propulsion systems that are currently in development and testing for space.
Emerging Applications: Thus, satellites will assume an even greater role in our future. Space tourism will be able to reach more people. Internet services from space are expected become more accessible, thus providing global access to even the most remote areas. Satellites can also be employed for resources tracking, and asteroid mining and perhaps, habitat on other planets.
A Day in the Life of a Satellite: Think of how a satellite feels, moving around the world at thousands of miles per hour. You get to see sunrises and sunsets every ninety minutes, you watch the weather phenomena down below while sending signals that link people from one continent to the other. They are used to record scenes of deforestation, melting of glaciers and even an array of ships at sea.
Satellites and the Future of Humanity: The future belongs to satellites when it comes addressing some of the most pressing issues facing humanity today. They can assist in preventing or observing weather changes, controlling natural disasters, bridging the existing gap between the online and offline world, and transform space exploration possibly resulting in new settlements on other planets. The opportunities are endless as space itself.
FAQs
Q1. What keeps a satellite in orbit?
A: It is due to the balance between gravitational force towards Earth and the centrifugal force away from Earth. They are in continuous freefall towards the Earth but move forward at such a speed that they keep missing it that results in a stable orbit.
Q2. How are satellites launched into space?
A: Rockets are used to put satellites into orbit. These rockets usually consist of several stages that kick out in order to overcome Earth’s gravity. After a rocket brings its load to space, the satellite is sent on its way and positioned in its planned orbit.
Q3. How do satellites communicate with Earth?
A: To pass the received and transmitted information, satellites use radio frequencies mutually to ground stations on Earth. Included in these signals are the pictures, voice, and sound being transmitted to the satellites.
Q4. How long do satellites last in space?
A: The lifespan of a satellite often ranges from 5 to 15 years but it may vary with different conditions. Factors like orbital environment, fuel limits, and technological obsolescence impact their duration.
Q5. What happens to old satellites?
A: Decommissioned satellites, if low enough, may re-enter Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. Some are sent moving to the “graveyard orbit” while others are left there as space debris to be managed and watched to avoid damage with intimating satellites who are functional.