Impact of Dark Energy: Exploring the Consequences and Implications
What is Dark Energy?
Dark energy is an unseen force that occupies the whole universe and acts on galaxies leading to accelerated expansion of the universe. It is not like other types of energy or matter and its true properties remain one of the most important unsolved questions of the modern cosmology. Despite judging its impacts, both positive and negative, its core is still impossible to comprehend.
The Expanding Universe
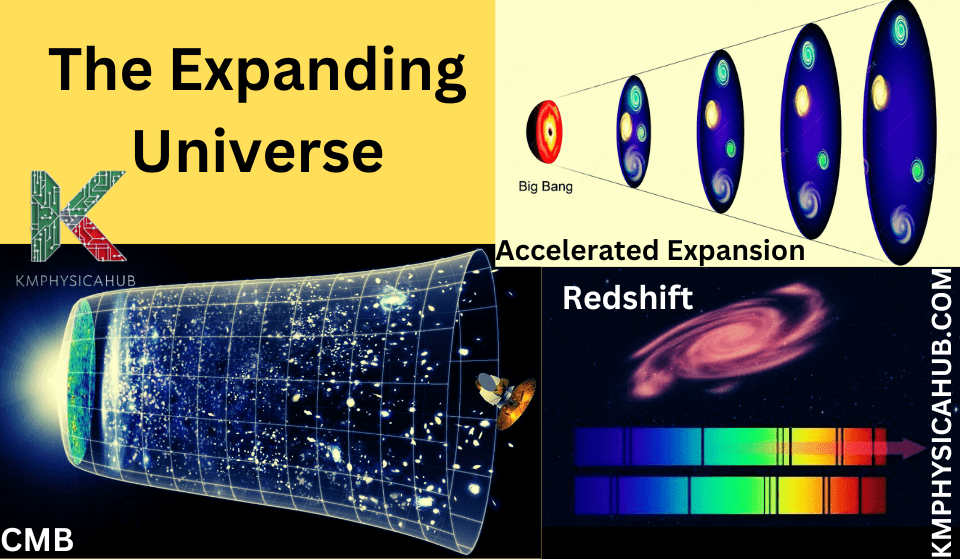
The fact about the expansion of the universe is beyond doubt and quite well understood with evidences from distinct observations. Edwin Hubble in the 1920s observed that what appeared to be distant galaxies was actually objects receding from earth and the rate of their spaceflight increased the further they were. This is known as Hubble’s Law. It gave concrete evidence to accept the theory that the universe is expanding.
Evidence for Expansion:
Redshift of distant galaxies:
The spectrum of most of distant galaxies shows that their wavelengths are shifted to the longer end, which indicates that the galaxies are moving away from us.
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB):
CMB stands for Cosmic Background Radiation which is a faint residual of Big Bang. It exhibits tiny rhythmic fluctuations of temperature which could be explained only if the universe used to be denser and much more compact in size.
Unexpected Acceleration:
While the expansion of the universe was initially expected to slow down due to the gravitational pull of matter, observations in the late 1990s revealed a shocking truth. The expansion of the universe is said to have been accelerating. This accelerated expansion, discovered through measuring the red-shift of light from distant supernovae, indicated the effect of a repulsive force over gravity and pushing the increase out even further. This mysterious force is called dark energy.
Nature of Dark Energy
Cosmological Constant:
There are lots of proposed explanations for dark energy and one of the earliest theories is the cosmological constant idea given by Albert Einstein. In his theory of general relativity, this constant was introduced to represent a static universe since the opinion at the time was that the universe was not expanding. This constant was later regarded by Einstein as his most significant mistake, and then it emerged in the context of dark energy as a possibility.
The cosmological constant is the density of energy per unit volume and resists against the force of gravity by acting as a repulsive force. This constant energy density would be uniformly spread across the universe and cause its expansion to accelerate continuously.
Quintessence:
Another form of dark energy is known as the quintessence which is not like the cosmological constant in the sense that it is not constant but varies with time. This theory holds that the dark energy is a scalar field that fills the universe and interact with itself and with other particles as does the Higgs field.
The energy density of quintessence is not a constant but it depends on the value of the scalar field and so, can explain the observed acceleration of the universe. Such behavior enables the concept of quintessence to change over time, which may result in different rates of evolution in the past and in the future.
Other Theories:
Apart from cosmological constant and quintessence, some other explanations for dark energy are as follows:
Modified Gravity:
This theory postulates that current theories of gravity are insufficient and gravity works at large scale in a different way, and this new way emerged from laboratory experiments may explain the accelerating expansion without postulating the existence of dark energy.
Vacuum Energy:
In quantum field theory, vacuum is not entirely devoid of particles but contains virtual particles that occupy the space and enhance the energy density. This vacuum energy could potentially contribute to dark energy.
These alternative theories are still being developed and are yet to be fully proven or supported.
Evidence for Dark Energy
Supernova Observations:
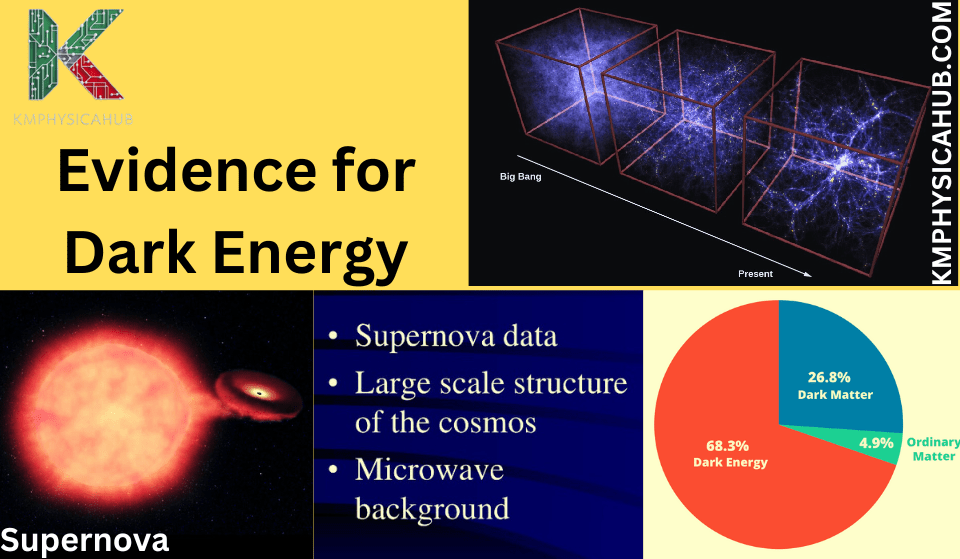
The detection of dark energy was made depending on Type Ia supernovae, which are highly energetic explosions of white dwarfs. These supernovae do have fixed brightness at their peak and this property makes them a standard way of estimating distances in space.
During the late 1990s, two groups of astronomers separately discovered that using Type Ia supernovae seemed to be intrinsically fainter than previously believed. This observation did not tally with the prediction of the slowing down of the universe’s expansion and gave indications of the accelerating expansion due to an unknown factor.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation:
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation also supports the presence of dark energy. The CMB is a residual radiation from the Big Bang which exhibits a temperature pattern that can be studied to provide details of the expansion of the universe.
The exact measurements of the CMB especially the mass ratio of baryonic to dark matter points to the requirement of dark energy to account for the observed expansion of the universe. Analyzing the temperature fluctuations detected in the CMB radiation, scientists were able to determine that the universe is made up of about 5% ordinary matter, 25% non-luminous or dark matter and 70% dark energy.
Large-Scale Structure:
The existence and distribution of galaxies and matter around a diverse universe are counted to prove the dark energy model. The overall distribution of galaxies and the overall structure of the large-scale universe can be illustrated as a cosmic web made of dense filaments and large voids. Such a complex pattern can be due to the impact of gravity and dark energy.
It is like a fabric of the universe created by the dance of gravity and dark energy. Dark energy is responsible for pushing matter away, forming voids and the general layout of the universe while gravity is responsible for holding matter together leading to the formation of clumps or filaments.
Impact of Dark Energy on the Universe:
It is not just an abstract idea of how the universe can be filled with something intervening in the cosmic processes but it is an active element influencing the ultimate destiny of the universe. This scenario works as a conductor to coordinate the refining of the universe and the formation of galaxies and large-scale structures.
-
Accelerated Expansion:
Repulsive Gravity ( A Driving Force) :
Dark energy has strange properties, it is similar to an anti-gravity force that pulls galaxies and clusters of galaxies apart. This force stands in contrast to gravity, and rather than diminishing over vast distances, increases as the universe expands – resulting in accelerated expansion.
For instance, you can try to picture a balloon with air inside it, in which little dots are galaxies. When you blow more air into the balloon, the dots get separated and the frequency of their separation escalates. This is similar to what has been happening with the universe that is expanding at a faster rate due to dark energy.
The Cosmic Horizon:
The accelerated expansion of the universe has profound consequences: it has actually painted a boundary, a line that cannot be crossed, a veil that is drawn in front of the cosmos. With time and space expansion, distant galaxies merely emit light that is stretched and red-shifted to a level where it is no longer observable. This means that there are areas of the Universe that will always be unreachable and inaccessible for further exploration.
Suppose, for example, visualizing a fog that settles on the horizon and blurs the contours of the landscape. In the same manner, the assumption that the universe is increasing its rate of expansion gives birth to a cosmic fog that hides the far off universe from view.
The Isolation of Galaxies:
The larger the universe becomes, the farther apart galaxies are from each other in space. This isolation is due to the fact that the rate of expansion is now much faster and galaxies are torn apart from one another, so they can no longer merge to build new structures.
Picture a group of friends who are loosing their bond with each other because of age and geographical location differences. Likewise, galaxies are getting more and more detached from each other due to the expansion of the universe.
-
The Fate of the Universe:
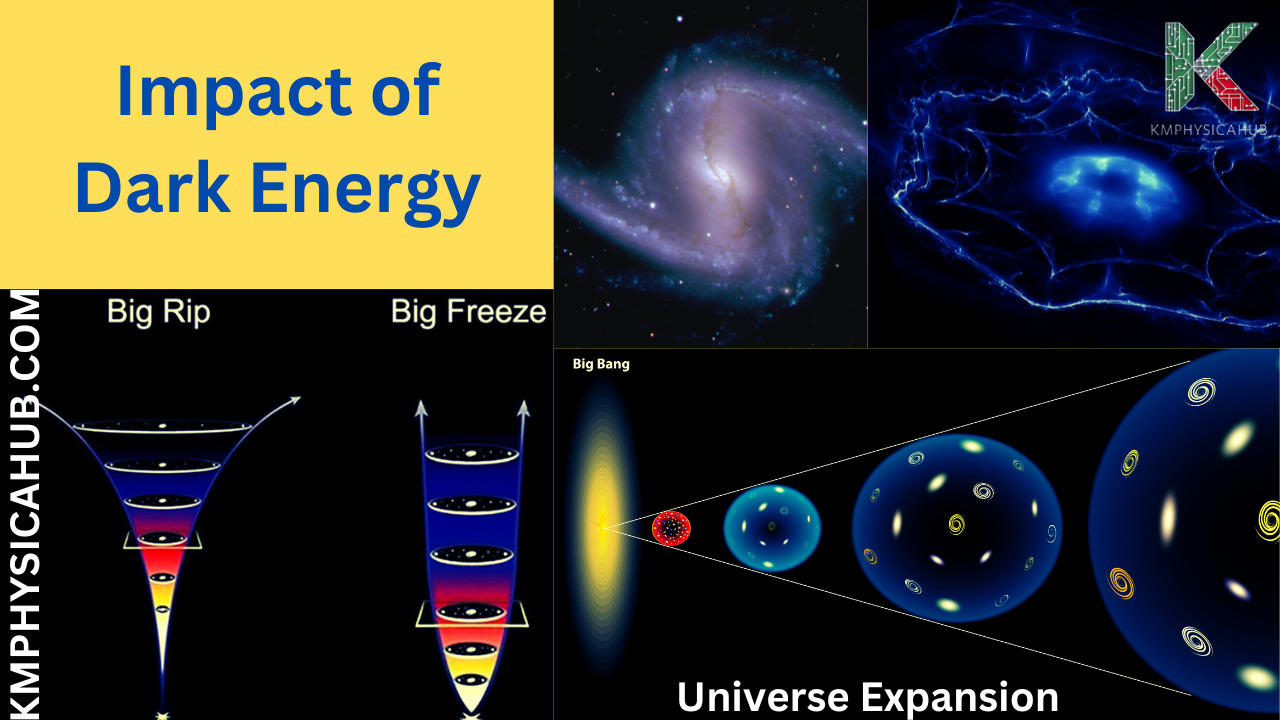
The Big Rip:
There is another possible future for the whole universe based on dark energy called the Big Rip. In this case, the acceleration continues to rise until it becomes incredibly immense to the extent of overcoming the gravitational forces that bind galaxies, stars, and even atoms. The universe would then rip itself apart, with all matter and energy disintegrating into a cosmic soup.
Consider the image where a piece of fabric is ripped by some force. Likewise, the Big Rip would practically explode the universe and all that would remain would be chaos and a cosmic void.
The Big Freeze:
Another possible future is the Big Freeze, more formally known as the heat death of the universe. In this case, the expansion keeps on accelerating, although at a pace lower than the Big Rip. Finally, the universe cools down, turns dark, and dies with galaxies spread out to great distances and no new stars being born.
Think of the fire that is gradually dying down and the only thing remaining is a charcoal. Likewise the Big Freeze would make the universe cold and dead, with no energy or movement.
The Uncertain Future:
The fate of the universe is still unknown and the Big rip and the Big freeze are only a few theories of what could happen. While the concept of dark energy is still relatively unknown, and its role in the expansion of the universe is also not clear, future investigations may shed new light on the circumstances of the universe’s destiny.
-
Impact on Structure Formation:
Slowing of Growth:
Dark energy interferes with the ability of galaxies and large structures to form because it causes the decrease in the growth of fluctuations in the early Universe. Dark energy is repulsive and works against gravity, meaning that it will be harder for matter to form structures and groups.
Consider a sculptor employing efforts to shape the clay but there is an external force which pushes the clay away making it impossible to give it a particular shape. Similarly, dark energy alters the cosmic expansion to prevent the formation of structures within the universe.
Future of Structure Formation:
It is unclear what the formation of structure will look like in the future, and this depends on the effects of dark energy on the expansion of the universe. In case dark energy continues to pull the universe apart, structure formation should be halted resulting in a universe filled with galaxies but clusters are fewer. Conversely, if dark energy decreases or disappears, gravity can again pull matter and energy together, resulting in the development of new formations and denser cosmic fabric.
The Cosmic Web:
The cosmic distribution of galaxies into great walls, filaments, and voids is evidence to the interplay of gravity and dark energy in the cosmos. This cosmic web is not a static entity but it is always under the process of changes due to these two forces. Studying the large-scale structure also reveals features of dark energy and its effect on the further evolution of the universe.
Innovative and Interesting Sections
Dark Energy and the Multiverse:
The notion of a multiverse, a set of multiple universes, has provoked contemplation of many people. Certain theories propose that dark energy can somehow participate in the formation or the isolation of these universes. Think of an extent that is cosmic where other universes are created and developed, possibly under the action of dark energy and dark matter including black holes. This is of course all hypothetical and speculative, but it definitely throws the door wide open for understanding the formation and nature of the universe in which we live.
Dark Energy in Popular Culture:
Dark energy has become a part of science fiction and popular culture, creating numerous creative themes and enhancing our interest in the unexplained. Relating from the series “Star Trek” where expansion of the universe is depicted up to “Doctor Who” series where the theme of parallel universes is depicted, dark energy has become symbolic of the vast unknown universe. These fictional representations, which are based on science, are useful to remember that the potential between science and creativity is always an infinite one.
Dark Energy and the Search for Life:
The dark energy effects have implications for the search for other forms of life. Since the universe expands with galaxies moving away from one another, sending signals or traveling across the vast space between civilizations of stars becomes highly improbable if not utterly impossible. Nonetheless, the search for extraterrestrial life continues to be inspiring and learning how dark energy functions to form the universe can give useful information into the difficulty and potential of such a venture.
Conclusion:
The evidences for dark energy come from the supernova observations, cosmic microwave background, and the large-scale structure of the universe. This mysterious force, working like a repulsive gravity, has deep consequences toward the destiny of the universe with the prospect of an accelerating expansion and a progressively more lonely universe.
However, there are still numerous unanswered questions regarding the dark energy. What is it actually? Is it one of the principal forces in physics, or an example of some other form of interaction? What was its origin and what was its role in the earliest universe? These are some of the mysteries that remain unsolved and enhance the theories and imaginations of cosmologists.
FAQs
Q1. Define dark energy?
A: Dark energy is defined as an unknown form of energy that is believed to constitute 70% of the density of energy around the universe. It behaves like an outward pressure, thus pushing the universe to expand at a faster scale.
Q2. How is the existence of dark energy determined?
A: Research of supernovae occurring at cosmological distances indicates that the universe’s expansion rate has been increasing. This cannot be attributed to gravity. This acceleration is said to be caused by the dark energy.
Q3. Write two possible explanations for dark energy?
A: The first is the cosmological constant that is a sort of the constant energy density of the universe. The second possibility is quintessence, which is a field that evolves with time.
Q4. How is universe future affected by dark energy?
A: The accelerated expansion due to dark energy may result in Big Rip or the Big Freeze where the universe slowly disperses into nonexistence.
Q5. How does dark energy affect structure formation?
A: Dark energy opposes gravity by reducing the formations of structures such as galaxies and clusters. Thus, it prevents new structures from forming and stop matter from clumping together as easily.