Plant Growth and Light: What You Need to Know about Color, Intensity, and Duration
The sun is an essential factor in growth and development of plants due to light. It is involved in photosynthesis that is very important in the production of energy for plant growth, development and reproduction. It is especially important for disciplines like agriculture, horticulture, or even indoor gardening to know how light affects plants. In this article, the various effects of light on the growth of plants shall be analyzed in accordance to aspects like, intensity of light, quality of light, the duration of light and light periods.
Role of Light in Plant’s Growth
Energy from light favors plant growth, and the flower formation process by triggering photosynthesis among other processes. It is a source of energy used for food production, germination of seeds in plants and other vital processes in growth of plants. Let’s delve into the details:
-
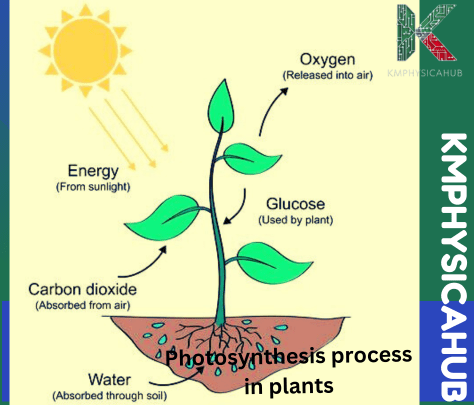
Photosynthesis and Energy Production:
Photosynthesis is the process through which solar energy is converted into glucose, the energy storage molecule of cells, using chlorophyll to do so. Its equation is given as:
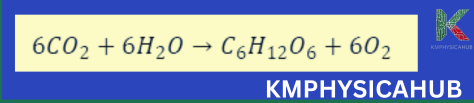
Carbon dioxide and water are converted using chlorophyll and sunlight into glucose for growth and the oxygen is removed, freeing it up in the atmosphere needed by many different species. Chlorophyll, the green pigment present in the leaves of a plant is responsible for getting light energy in this process. Magnesium cannot be produced by plants that require chlorophyll and phosphors to form proteins.
Lighting intensity thus has and impact on photosynthesis process. More intense light generally leads to faster growth.
-
Direction of Growth:
The plants which grow in the outdoors tend to navigate towards the light source, which is generally sunlight for the purpose of performing photosynthesis. However, some plants move in response to a stimulus; this can be observed in the plants that follow the direction of the sun throughout the day, a phenomenon referred to as heliotropism.
-
Light Spectrum:
Various light wavelengths have distinct functions in the growth of plants:
Blue light: Essential for chlorophyll production and overall growth.
Red light: Promotes flowering and fruiting.
Full-spectrum light: Ideal for overall plant health.
-
Indoor Lighting:
Interior gardening, for example, hydroponics, requires artificial light sources – LED grow lights that replicate natural light to foster plant development and health. There should always be an appropriate duration of light referred to as photoperiod since some plants bloom based on the amount of light available per day.
Remember, light is one of the key components that are important to plant health, and understanding its impacts is useful to improve plant yield and health.
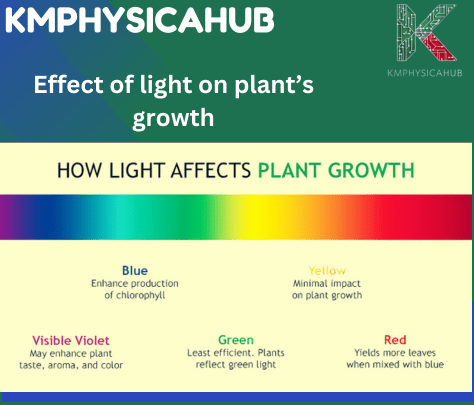
Effect of Light Color on Plant’s Growth
The color of light significantly impacts plant growth and appearance. Let’s explore how different light colors affect plants:
Red Light (600-700 nm):
- Promotes stem and leaf elongation, making plants taller.
- Encourages flowering and fruit development.
- Used in greenhouses to enhance growth.
Blue Light (400-500 nm):
- Promotes root development, chlorophyll synthesis and is involved in photosynthesis processes.
- Vital for vegetative growth and leaf formation.
- Commonly used in indoor grow lights.
Green Light (500-600 nm):
- Not as effective for photosynthesis.
- Plants appear green because chlorophyll a and b molecules show no absorption of green light.
- Acts as a protective light without contributing much to growth.
Far-Red Light (700-750 nm):
- Stops the growth of the stem while encouraging growth of the leaves.
- Used in shade avoidance responses by plants.
Adjustment of Light Color for Growth Needs:
To tailor light colors for specific plant needs, consider the following strategies:
- Select the Right Light Source:
LED Grow Lights: These allow you to select and change light spectra by regulating the output of red and blue diodes. Select the appropriate spectrum for the development cycle of the plant whether it is in the vegetative stage or flowering stage.
Full-Spectrum Lights: These are close to natural light and come with varied spectrum colors.
- Adjust Light Duration (Photoperiod):
Different plants have varying light requirements. Some need longer days (long-day plants), while others thrive with shorter days (short-day plants). Use timers to maintain consistent light cycles.
- Color Filters:
Attach colored filters (e.g., red or blue) to standard white light sources. This modifies the light spectrum reaching the plants. For flowering, use more red light; for vegetative growth, add blue light.
- Distance from Light Source:
Place the light source at an optimal distance from the plants. Too close can cause damage; too far reduces effectiveness. Adjust based on the plant’s light sensitivity.
- Rotate Plants:
If using directional light (e.g., sunlight through a window), rotate potted plants regularly to ensure even exposure.
- Observe Plant Responses:
Monitor plant growth, leaf color, and flowering. Adjust lighting as needed. Yellowing leaves may indicate insufficient light.
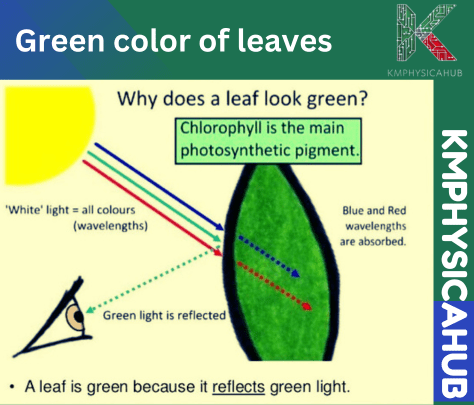
Why do Plants Look Green?
Chlorophyll, the green pigment molecules in the plant, absorbs red and blue colors in the light while reflecting green color and that is why plants appear green from our perspective. Some pigments (such as carotenoids) play roles in other colors, including yellow and orange colorations.
Factors of Light Affecting Plant Growth:
In plant’s growth, light plays an important role. Let’s explore how different aspects of light influence plants:
Light Quantity:
- Intensity: The concentration of sunlight affects photosynthesis. More light generally leads to better growth.
- Manipulation: You can increase light by using reflective materials or supplemental lights. Decrease it with shading.
Light Quality:
Color (Wavelength): Sunlight contains a full spectrum, including red and blue light.
Effects:
- Blue light: Promotes vegetative growth (leaves).
- Red light: Encourages flowering.
- Green light: Plants reflect it, appearing green to us.
- Choosing Light Sources: Fluorescent lights (cool white) are great for seedlings, while incandescent lights produce too much heat.
Some Common Signs of Insufficient Light in Indoor Plants
When indoor plants don’t receive enough light, they exhibit several signs. Here are some common ones:
Sparse or Leggy Growth:
- New leaves grow far apart, resulting in a thin, straggly appearance.
- The distance between leaves (internodal distance) increases.
- Solution: Provide more light to prevent leggy growth.
Leaning Towards Light Sources:
- Plants bend or lean toward windows or brighter areas.
- Leaves may face the light source.
- For even exposure, rotate your plants on a regular basis.
Small Leaves:
- Insufficient light leads to small, underwhelming new leaves.
- Light is essential for energy production and larger foliage.
- Consider adjusting light conditions.
Lack of New Growth:
- If your plant hasn’t grown for months, it likely needs more light.
- Energy from light fuels growth.
- Ensure adequate light exposure for thriving plants.
Effects of Artificial Lighting on Plant Growth
The effects of artificial lighting on plant growth are rather varied and may act both directly and indirectly. Let’s explore some key aspects:
Spectral Effects:
- LED Technology: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as supplementary light in greenhouses have advanced significantly.
- Light Spectra: Different LED spectra can shape plant morphology, enhance protective metabolites (for better food quality), and potentially trigger defense mechanisms.
- Challenges: Transferring controlled environment knowledge to greenhouses is complex due to natural light variations and species-specific differences.
Specific Effects:
- Red Light: Promotes seedling growth, lateral branching, and delays flower bud differentiation.
- Far-Red Light: Counteracts red light effects.
- Blue Light: Inhibits leaf growth and reduces overall plant size.
Indoor vs. Natural Light:
- Stunted Growth: Indoor artificial lighting can hinder plant growth.
- Natural Light: Direct sunlight indoors is critical for optimal plant development and improving our living environment.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Using Artificial Lighting
When it comes to artificial lighting, some avoidable mistakes can greatly improve your home’s lighting.
- Mismatched Bulb Temperatures:
Using bulbs with varying color temperatures in the same room can create an inconsistent ambiance. Aim for consistency across fixtures by choosing warmer or cooler bulbs.
- Over-Reliance on a Single Light Source:
Depending on the main light source can cause the room to be slightly lit with shadowy areas. Position lights for layering and use task, accent, as well as ambient light sources to achieve functionality.
- Improperly Sized Fixtures:
Lack of proportion is created when the fixtures selected are either larger or smaller than the room. Location and size of the room, and height of the ceiling should be considered while choosing lighting.
- Neglecting Dimmers:
There is a flexibility in the use of dimmers depending on the amount of illumination to emit. Make use of dimmer switches since this will enable the house to adjust the lighting to suit the activities or even the mood at any time.
- Ignoring Task Lighting:
Accent lighting or general lighting in task areas is crucial, for instance, reading lamps, under-cabinet lights, etc. Even desks, kitchenettes, or places for reading should not be out of the question.
Conclusion:
Plant requires light for its growth ad development; light affects all the developmental processes in plants from photosynthesis to flowering. Based on the light intensity, quality, and duration and knowledge of photoperiodism, we can produce better health plants and increase the productivity. Sheltered agriculture, horticulture, and indoor gardening show that proper light is invaluable for improving the quality of the plants and increasing their productivity.
FAQs
Q1: What happens if a plant does not receive enough light?
A1: Lack of light causes low photosynthesis and thus poor plant development, chlorosis and in some cases plant demise.
Q2: Can plants grow under artificial light?
A2: It is quite possible to grow plants using artificial light as long as the type of light used provides the optimum wavelength for photosynthesis and any other processes in the plants.
Q3: How does light quality affect plant growth?
A3: Based on the wavelengths of light, or colors, a particular plant part is influenced in one or many ways. Blue light enhances the process of photosynthesis that leads to the development of the leaves, on the other hand, red light plays a major role in floral initiation and in the generation of fruits.
Q4: Why is the duration of light exposure important for plants?
A4: Light is used by plants for different mechanisms and, like anything else, they require some time of darkness to continue their metabolic processes. Day and night change are essential for growth and development.
Q5: What is photoperiodism and why is it important?
A5: Photoperiodism is the effect of day and night length to control flowering an growth stages in plants. This has been understood in helping when it comes to plant growth and flowering time dimensions.