Effect of Light Pollution on Humans, Environment, Plants and Wildlife
What is Light Pollution?
It is an illumination that occurs at night due to artificial light, commonly referred to as light pollution or artificial light at night (ALAN). It takes place when excessive artificial lighting is cast on the night skies thereby masking natural blackness. This is a fairly modern problem that is associated with the use of electricity particularly in lighting in the 20th century.
The Growing Problem of Light Pollution:
Artificial lighting at night continues to rise in the population, and it is approximated that it has a cut across more than half of the global geography.
- Urbanization: As cities grow, they generate more artificial light.
- Economic Development: In many countries as the processes of industrialization and modernization, widespread electric lighting is adopted.
- Technological Advancements: Although advanced and more efficient lighting systems can be introduced and used effectively they also cause light pollution as time progresses.
Light pollution has much more profound impacts other than mere disturbers of aesthetics. It has detrimental effects on the biological communities, animals and ultimately human beings.
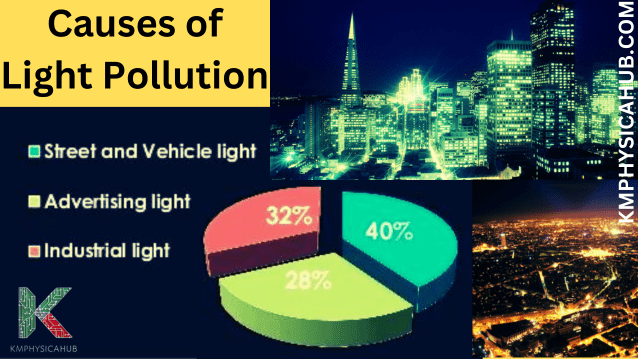
Causes of Light Pollution
-
Artificial Light Sources
Street Lighting:
A way in which artificial lighting has been erected to provide safety and visibility to road users become one of the primary sources of light pollution.
Types of Streetlights: They include; Incandescent, fluorescent, High Intensity Discharge (HID) lights and Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs).
Technologies: Most technologies give different levels of light output, efficiency and color temperature.
Light Pollution Impact: Many streetlights discharge light in all directions, particularly up, making them a big source of sky glow and light trespass.
-
Building and Architectural Lighting
Light-emitting structures, especially those with exterior lit signs and lighted structures, are responsible for most of the light pollution.
Excessive Lighting: Excessive use of artificial lighting on structures, especially for purposes of decoration is one way through which light pollution is created.
Poorly Designed Lighting: Since light from a poorly directed lamp can spill to the night sky and adjacent zones, it needs proper direction towards the ground to avoid light pollution.
-
Commercial Lighting:
Retail shops, advertising boards, and car parks are some of the most common illuminated areas where people frequently visit and require a clear view of surroundings.
Billboards: A typical example of a light source that affects a large population is billboards, particularly those emits bright lights along the main roads or populated regions.
Storefronts: Excessive illumination of storefronts can pose a threat to the environment .
Parking Lots: Lighted parking lots, when not adequately shielded, tend to cast light up in the air causing sky glow and trespass.
Impact of Different Light Sources
The impact of light pollution varies depending on the type of light source:
White Light: One of the biggest issues with white light, especially with LED lights, is that this type of illumination is extremely noticeable to wild animals and therefore disrupts the natural functioning of these species to a greater extent.
Blue Light: Each day, many people are exposed to blue light coming from most modern electronic devices that interfere the human sleep-wake cycle.
Warm Light: White light such as the light produced by older incandescent bulbs, has a lesser impact on nocturnal animals but it also causes light pollution.
Effects of Light Pollution
Effects on the Environment
-
Disruption of Nocturnal Ecosystems:
Night light pollution affects the normal life cycles of nocturnal animals, plants, and insects.
Navigation: Animals that are active at night rely on the stars and the moon. These celestial signals are sometimes masked by light pollution causing disorientation that results in accidents.
Predation and Foraging: While hunters need darkness to help them pursue their prey, the prey on the other hand needs darkness to ease their escape. Contrary to this balance, light pollution can affect these predator-prey relations.
Reproduction: Most creatures that are active at night utilize dark environments for reproduction. Due to light pollution, these processes can be disrupted which reduces the chances of reproduction.
-
Impact on Biodiversity:
Light pollution affects biodiversity because it disrupts the natural system which affects both fauna and flora.
Population Declines: Light pollution can negatively impacts nocturnal species’ population that result in various food chain disruptions and general ecosystem damage.
Habitat Loss: It may produce areas of light that affect the habitat of night animals, which are left with no choice but to move to places that are still dark.
Extinction Risk: In severe conditions, it plays a part in the extermination of the endangered species that can only emerge at night.

Effects on Wildlife
Light pollution has specific impacts on various wildlife species:
-
Migratory Birds:
The stars help birds to locate the direction at night during migration. Most birds navigate their way using natural light and thus streetlights and other artificial lights mislead them to wrong paths where they can fly for days in circles leading to collision with buildings and death due to exhaustion.
-
Sea Turtles:
Baby sea turtles find their way to the water by following the moonlight after hatching. Artificial light cast by coastal structures disrupts the hatchlings by directing them inland and thus leading to their death
-
Insects:
Street lights encourage insects to be active in one area and affect their migrations or reproductive cycles. There is the risk of reduction in insect populations which are very essential pollinators and are important when it comes to food chain.
Effects on Plant Life
Effect of light on plant’s growth is a matter of consideration. Artificial lighting can impact the period of development and the occurrence of blooms, pollination as well.
-
Alter Plant Growth:
Street lighting can disrupt the natural darkness of the night to plants thus causes alteration of the photoperiod.
-
Reduce Flowering:
There are plants that have demands for flowering during the dark. Artificial light can inhibit or suppress flowering and this affects pollination and seed setting.
-
Disrupt Pollination:
Some insects use darkness to release pollen on plants or in flowers. This disrupts their activities at night and leads to reduced pollination and hence impacts plants reproductive mechanisms.

Effects on Astronomical Observation
Since the impact of artificial light on the night sky is considerable, it greatly impacts astronomy and other activities that involve observing the stars. This artificial light acts as a glow from the cities and other man made structures making it difficult to observe dimmer stars and other objects in the sky. It is a challenge faced by astronomers as they are unable to easily analyze and observe distant galaxies and nebulae among other astronomical objects.
Effects of on Human Health
-
Sleep Disruption and Health Problems:
Sleep Disorders: It interferes with the natural secretion of melatonin which is naturally produced hormone that controls the sleep in the human body. This can lead to conditions such as insomnia, disruption of sleep, and other sleeping disorders.
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: If one suffers from interrupted sleep, then chances of getting into some form of diseases such as obesity, diabetes, heart diseases, and specific types of cancer will have greatly risen.
Impaired Cognitive Function: Sleep is essential to the body and when one misses it the brain is the first organ to suffer and hence confusion, poor memory and reduced effectiveness are caused.
-
Impact on Mental Health:
Light pollution may also contribute to the occurrence of social and mental disorders.
Increased Anxiety: Night lighting has a potential of increasing the anxiety level of people as compared to that under natural light.
Mood Disorders: It has been known to cause several psychological disorders such as depression because of the increased level of illumination at night.
Sleep-Related Mental Health Conditions: It also leads to aggravation of other mental disorders including anxiety and depression.
Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
-
Shielding and Directional Lighting:
Shielded lights and downward-directed lights are the most effective methods in eliminating light pollution.
Shielded Lights: Shielded lights have a hood or some other cover that restricts the light emitted in the upward direction towards the sky.
Directional Lighting: Shining the light down towards the floor prevents the emission of light into the sky which might be useful in different aspects from happening.

-
Regulations and Policies:
Government regulations and policies are crucial in eliminating light pollution.
Light Pollution Standards: Establishing specifications of the amount of intensity that can be allowed to be produced from various categories of lights.
Lighting Codes: Ensuing local building codes that demand the usage of shielded lights and other measures to minimize light pollution.
Enforcement Mechanisms: Designing programs through which light pollution standards can be observed and policed.
-
Public Awareness Campaigns:
Increasing awareness of the public on the problem of light pollution, is important.
Inform the Public: Inform the public about what causes light pollution, and what its effects are.
Promote Best Practices: Persuade the public and the commercial companies to reduce or reverse the effects of light pollution.
Inspire Action: Call individuals to action to solve and avoid the issues of light pollution in their society.
-
Citizen Science Initiatives:
Collect Data: Involve the citizens in collection of data on the intensity of light pollution taken in their area of residence.
Identify Problem Areas: Settle on the areas with high amount of light pollution by using data collected by citizens.
Advocate for Change: Call for the citizens to come out and demand for measures against light pollution in their areas.
Conclusion:
A global problem and global threat in the field of physics, light pollution is on the rise and is one that affects both the Earth and ourselves. It threatens the continuity of ecosystems, provides negative effects to wild life and even affects the overall well-being of humans. Night lighting is a measure that disrupts natural processes in the ecosystem and is adverse to wildlife and people’s physiology and sleep. Barrier lights, directional illumination, and restrictions involving light pollution are excellent counter measures. Awareness creation and citizen involvement can help individuals fight light pollution by applying changes in observance of public ordinances.
People Also Ask:
Q1. Define light pollution?
A: Light pollution is a concept describing the condition in which artificial light is used excessively and improperly, thus emitting light into the night sky and thus putting a barrier to true darkness. This can be due to bulb streetlights, buildings, billboards and other things if any exists in the neighborhood.
Q2. What are the impacts of light pollution?
A: Usage of artificial light:
- Interferes with the natural wildlife
- Has negative effects on human health
- Disrupts astronomical studies.
Q3. How can light pollution be reduced?
A:
- By using shielded lighting
- By minimizing unnecessary lighting
- By using warm white LEDs
- By supporting light pollution regulations
Q4. What is light pollution and light trespass?
A: The presence of too much artificial light in the environment is referred to as light pollution. While the light that illuminates the near by areas where it is not desirable is called light trespass.
Q5. How does light pollution affect wildlife?
A: It can negatively affect the behavior of the nightly active species by:
- Confusing them
- Hampering their feeding time
- Bringing them closer to their predators
- Changing their migratory routes.