How Mirrors Work, Types and Unreal Applications
In its simplest definition, a mirror is a flat, smooth surface that reflect light with minimal scattering and diffusion. For ages, humans have been intrigued by mirrors and their uses, whether for a practical purpose or an artistic one. Due to their capacity to reflect images, mirrors are important instruments in numerous activities ranging from simple personal grooming to higher scholarly projects. The formation of images in mirrors involves a combination of physical and psychological concepts that depend on the principles of light reflection, optics, and the nature of the mirror.
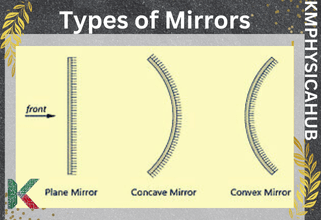
How are Images Formed in Mirrors
The general concept that makes mirror imaging is based on is that of reflection. It is always possible for light to either be absorbed by a surface, pass through, or bounce off a surface or material. Mirrors are mostly of glass backed with a metallic layer like aluminum or silver that is meant to reflect light. Likewise, as soon as light photons interact with the surface of a mirror, they are reflected in the normal course for a reflector in accord with the laws of reflection.
According to the law of reflection, the angle of incidence is the angle formed by the incoming light with the perpendicular to the reflecting surface while the angle of reflection is the angle formed between the reflected light and the normal. Normal is an imaginary straight line which is shown perpendicular to the surface.
Types of Mirrors
Mirrors come in various shapes and forms, each serving different purposes and creating different types of images:
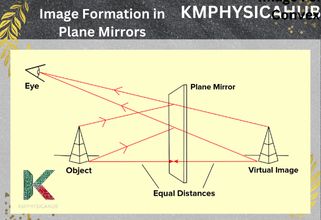
1. Plane Mirrors:
These are flat mirrors. Any image produced by a plane mirror is always a virtual image, it is always erect, and always the same size as the image itself. They are frequently used in everyday life at various places, e.g. bathrooms and dressing rooms.
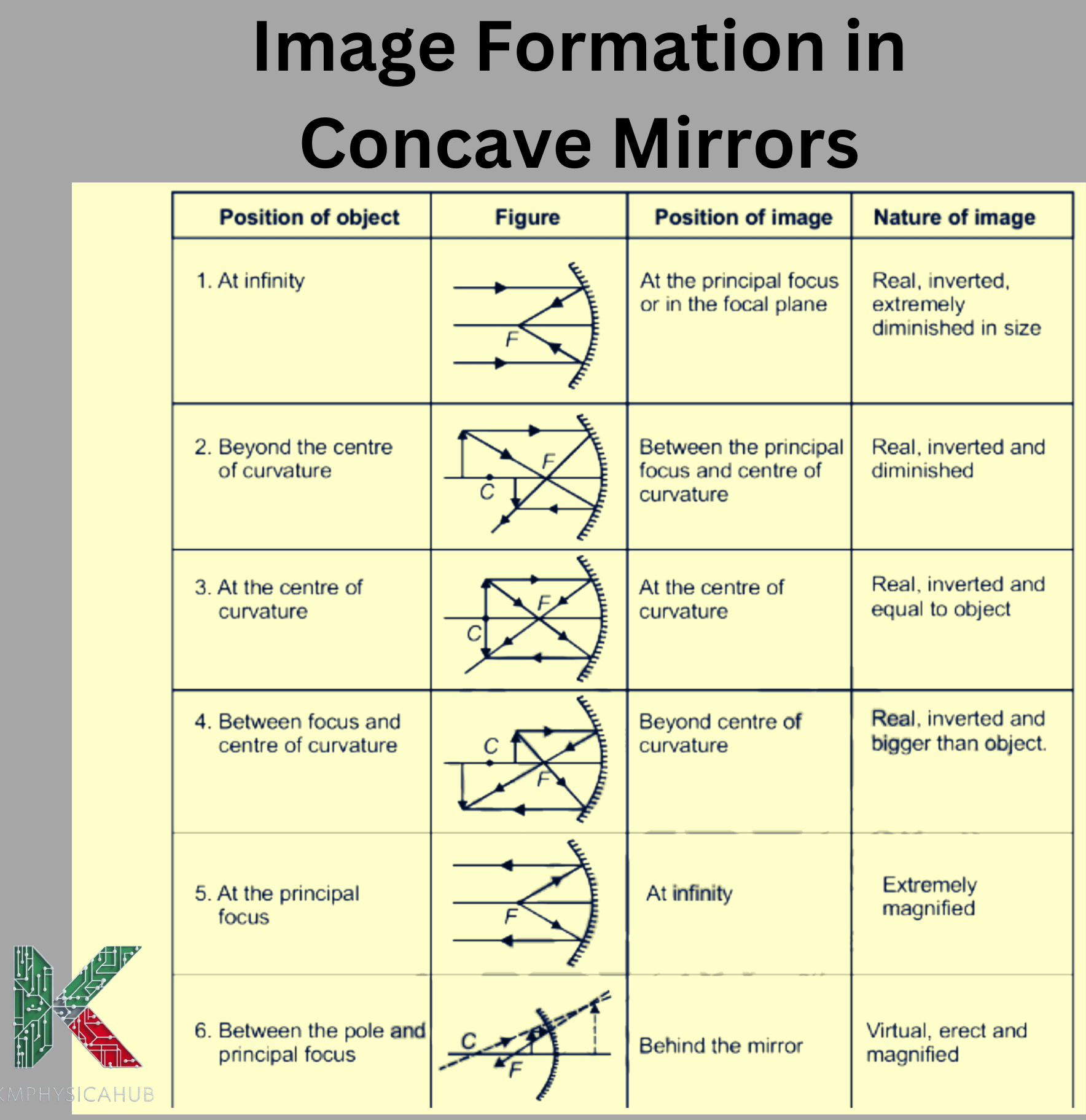
2. Concave Mirrors:
Concave mirrors are curved inwards and have a shape that looks just like the inner surface of a sphere. Based on the nature of its curve, concave mirrors can form real or virtual images behind it depending with the positioning of the object. These are applied in the construction of telescopes, shaving mirror and even the car headlight reflectors.
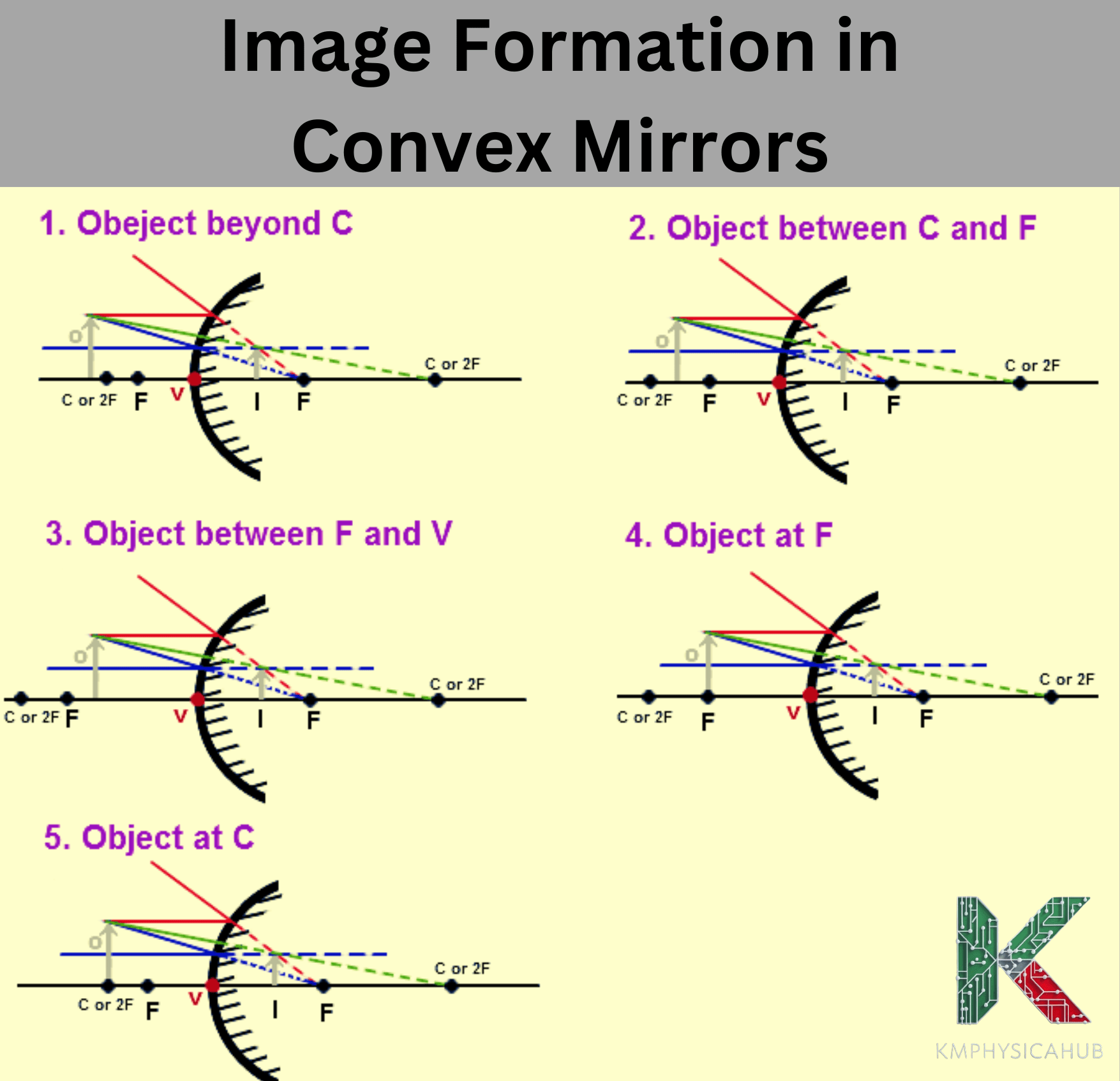
3. Convex Mirrors:
These are curved outward and always give virtual, diminished and upright images. Some of the uses of convex mirror includes use in vehicles especially as rearview mirror and security mirror since it offers wider angle view.
Factors Influencing Image Formation and Perception
Several factors determine how an image is formed and perceived in a mirror:
- Distance from the Mirror: The distance at which the object is placed in relation to the mirror determines the size, orientation etc of the image. For example, concave mirrors which are thicker in the center have the ability of creating an enlarged virtual image of objects located closer than the focal point while on the other end, a small real image of objects located at a distance greater than the focal point.
- Angle of Observation: The position at which one directs his or her eyes in relation to the mirror determines the image that is reflected on the surface. One can see that the Rice logo is reflected and if the viewer changes his or her angle of viewing slightly, some parts of the reflected image may be visible or invisible.
- Surface Quality of the Mirror: Surface irregularities on the mirror impact the outgoing reflection or the image formed on the surface of the mirror. Mirrors that have little or no imperfections such as cracks or abrasions on the silvering layer offer sharp reflection while those with such imperfections offer blurred reflections.
- Lighting: From the intensity and direction of light it is possible to significantly change an appearance of the image reflected in the mirror. Good intensity of light will improve the sharpness of the reflected image, on the other hand a faint intensity of light will degrade the visibility of the details.
- Perception: Mirror images are perceived differently from real life objects due to the knowledge on spatial orientation and perspective. The brain integrates the information received from both eyes and being able to accurately identify the distances and orientations of objects. This processing is based on cues like relative size, convergence, and accommodation, but mirrors challenge these cues by altering our perspective. Despite the inversion and distance, our brains adapt remarkably well to viewing images in mirrors.
Applications of Mirrors
In general, mirrors are used in multiple aspects of our lives and different activities. Here are some common uses:
Decorating: Mirrors have the effect of making a room appear bigger since it tends to give a double reflection of objects in the room. Interior decorators utilize them to provide a feeling of spaciousness, particularly in houses. Different mirror styles can also set a specific atmosphere in a room.
Safety: Reflectors are an absolute necessity when it comes to safety. For example, auto manufacturers fix side mirrors on vehicles to help a driver view adjacent traffic. Security personnel use mirrors to monitor areas like parking garages.
Vision Correction: Optometrists employ lenses which act like mirrors in order to cure vision. Glasses or contact lenses focus the light into the eye so that the retina forms clearer images.
Scientific Tools: Microscopes use lenses and telescopes use mirrors. These tools support research on entities that cannot be directly observed due to their size or distance from the observer.

Energy and Affirmation Techniques: In practices like Feng Shui, mirrors are believed to direct energy flow in buildings, reducing stress and promoting positive experiences. There are also other things that people can try such as speaking positive words in the mirror to increase self-esteem levels.
Photography: A startling discovery is that even when there is usage of digital cameras, traditional lenses do matter in the overall image quality. It produces light into the camera and it influences the final result as a whole.
Fashion Design: It has been observed that mirrors are used by fashion designers in order to see the different sides of clothing and accessories at once. In departmental stores there are often three-way mirrors so that customer could try on the clothes before buying them.
Unreal Aspects of Mirrors
While mirrors in the real world serve practical purposes, they can also be fascinating and even surreal in certain contexts. Here are some unreal aspects of mirrors:
Infinite Reflections: If you ever find yourself between two mirrors that are placed opposite each other, what you get is an image that extends to the horizon. It conveniently gives a feel of watching and navigating another world altogether.

Hall of Mirrors: There is the famous architectural feature like the Hall of Mirrors which is ornamented in the style of Palace of Versailles. It also has strategically located mirrors that are used to generate a perception of spaciousness and luxury. In fact, with Unreal Engine 5, game developers could build such environments with realistic reflections.
Planar Reflections in Games: Game engines like Unreal Engine use planar reflections to simulate mirrors. These reflections dynamically update based on the player’s movement and surroundings. Level designers and artists can create seemingly perfect mirror illusions which add to the overall feel of the virtual environment.

Conclusion:
Reflection of objects in mirrors presents an interesting phenomenon of image formation characterized by laws of reflection and behaviors of materials used in formation of mirror. From the basic plans and simple plane mirrors to the more complex curvatures of curved mirrors, the science is basic physics all the same. By studying how mirrors create images, we gain a deeper appreciation for the science that shapes our interaction with the reflective world around us.
FAQs
Q1. Why do plane mirrors produce virtual images?
Mirrors that are actually flat generate virtual images because the actually reflected rays do not converge; they seem to originate from a point behind the mirror.
Q2. Can a concave mirror produce both real and virtual images?
Yes, a concave mirror has the ability to form real and virtual images depending on the position of object in relation to the focal point and center of curvature.
Q3. Why are convex mirrors preferred for rear-view mirrors in vehicles?
Convex mirrors are chosen because they allow seeing more area around vehicles and reduce blind zones in comparison with flat mirrors.
Q4. What is lateral inversion in plane mirrors?
Lateral inversion means the change in positions of left and right in the image formed by a plane mirror.
Q5. Do convex mirrors magnify objects?
Convex mirrors do not enlarge objects, but rather make them seem smaller while revealing more of the surrounding area.